Team
RNA splicing, Cell signaling and Response to Therapies
Dpt: Microenvironment, cell plasticity and signalling
Our research activities
Béatrice EYMIN
Team leader
04 76 54 94 76
Our research axes
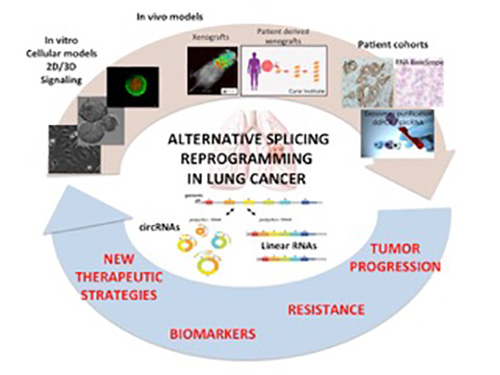
SR proteins are critical splicing factors. We previously showed that SR proteins are up-regulated in lung tumors. Our objectives are to deepen the molecular mechanisms by which SR proteins contribute to lung tumor progression and response to therapies. More specifically, we want to decipher whether and how SR proteins contribute to genomic instability and mutations in lung cancer cells which occur during therapeutic resilience through modulation of the DNA Damage Response and DNA repair pathways.
Learn morePharmacological inhibitors targeting different components of the spliceosome machinery constitute a promising therapeutic area in cancer. However, the molecular mechanisms supporting their anti-cancer effects remain largely unknown. Our objectives are to decipher whether the use of these inhibitors, either alone or in combination with chemotherapies, could be a way to counteract drug resistance in lung cancer.
Learn moreReceptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTK) including the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) play a key role in lung cancer progression. The use of tyrosine kinase inhibitor of EGFR (EGFR-TKI) is a very promising therapeutic approach with unprecedent results on patients survival. However despite its proven efficacy, resistance inevitably develops. Our objectives are to evaluate the contribution of RNA splicing reprogramming to the development of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI in NSCLC.
Learn moreCircular RNAs (circRNAs) belong to a new category of mostly non-coding RNAs which are very stable and detectable in liquid biopsies, making them promising biomarkers. In recent years, their role in the initiation and progression of cancers as well as in the response to treatment has emerged. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying their effects remain largely unknown. Our objectives are to deepen the role of circRNAs in the escape of lung tumors to treatment.
Learn moreOur major publications
See all publicationsOur activities in pictures
Our collaborations
- Pr Ester Hamond (Institute for Radiation Oncology, Oxford, United Kingdom)
- Dr Pablo Huertas (Andalusian Molecular Biology and Regenerative Medicine Centre, CABIMER, Seville, Spain)
- Dr Eleni Nikolakaki (Laboratory of Biochemistry, Aristotelian University, Thessaloniki, Greece)
- Dr Didier Auboeuf (ENS, Lyon)
- Dr Didier Decaudin (Institut Curie, Paris)
- Dr Martin Dutertre (Institut Curie, Paris)
- Dr Carmen Garrido (U1231, Dijon)
- Pr Nicolas Girard (Institut Curie/Montsouris, Paris)
- Dr Antonio Maraver (IRCM, Montpellier)
- Dr Franck Mortreux (ENS, Lyon)
- Dr Olivier Sordet (CRCT, Toulouse)
Our technologies
- 2D and 3D cell culture
- Proximity Ligation assay (PLA)
- RNA BaseScope
- RNA sequencing
- RT/PCR and quantitative PCR (QPCR)
- JESS
- Western blotting
- DNA Fiber assay
- Immunoprecipitation
- GST-pull down
- Immunofluorescence and Immunohistochemistry
- Flow cytometry
- Seahorse
- SIRF