Team
Cancer Targets and Experimental Therapeutics
Dpt: Microenvironment, cell plasticity and signalling
Our research activities
Our main objective is to define theranostic nano-vectors for the treatment of cancer, and in parallel to develop the corresponding medical devices to investigate them.
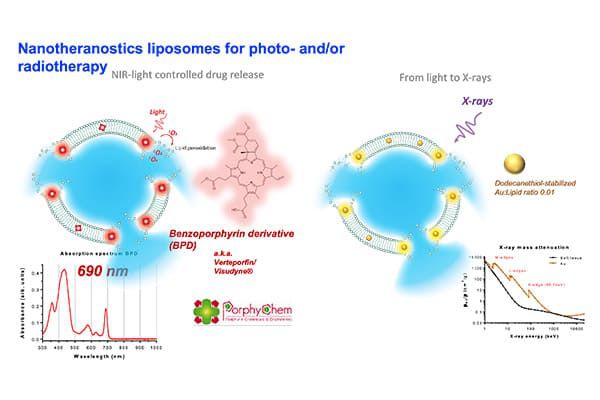
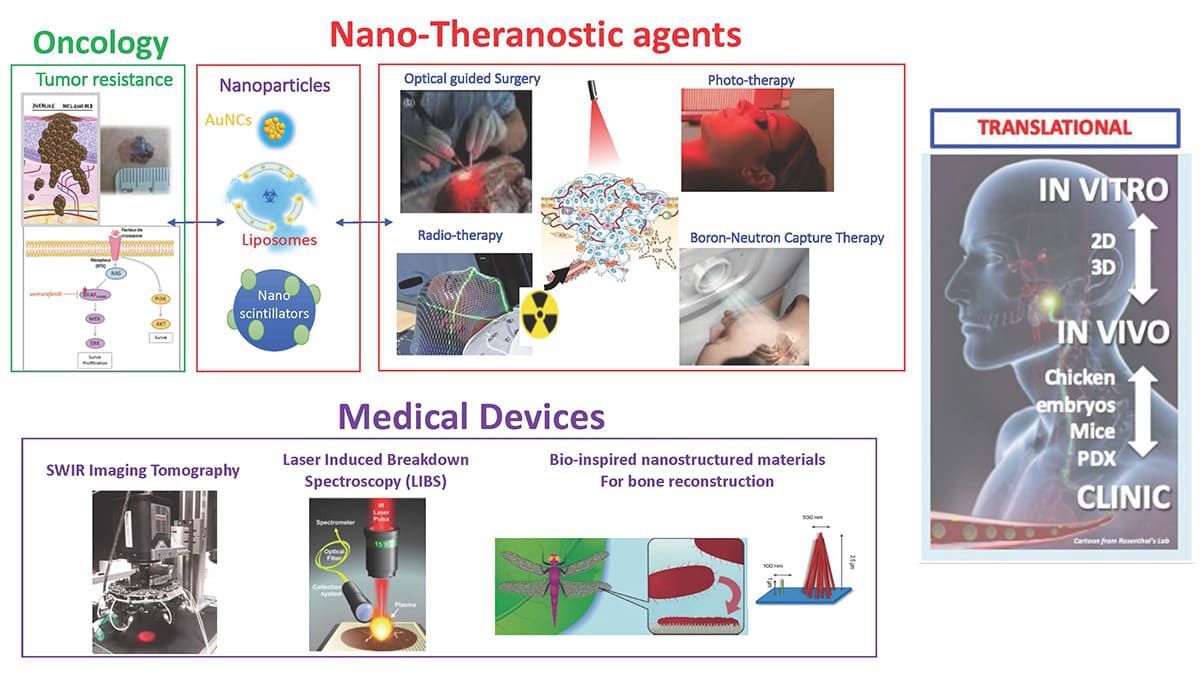
We develop nanoparticles (NP) that are 1/ detectable in the near-infrared windows (NIR I and NIR II (or SWIR)) and/or 2/ therapeutically active. More specifically, these NP are defined to escape the resistance mechanisms usually set up by tumors. For example, the NP we are investigating are designed to deliver drugs and/or potentiate the effect of photo- and thermal-therapies upon light excitation or radiation therapies, upon X-rays or neutrons excitations.
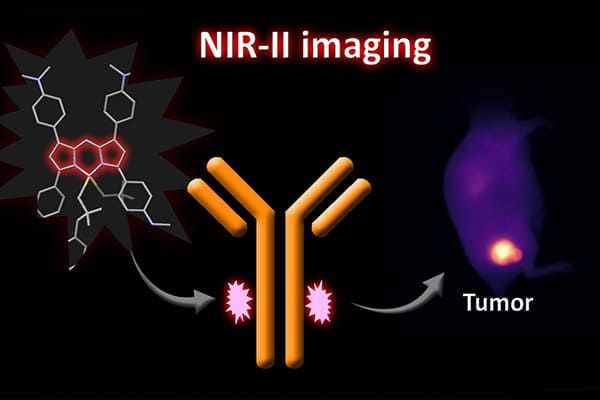
The fluorescent NPs we are developing are also used by our team of surgical oncologists and reconstructive surgeons to perform optically-guided surgery.
In parallel, we develop the instrumentation to detect and monitor these NPs using diagnostic instruments (LIBS; Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy) or in vivo visualization tools (Fluorescence Reflectance Imaging, NIR/SWIR Tomography).
Before considering a transfer to the clinic, the nano-vectors and instrumentation we develop are evaluated in vitro in 2D and 3D (microtumors ± microfluidics) before being tested in chicken embryo models or in preclinical cancer models grown in rodents.
Finally, all these technologies are made available to the scientific community via our nationally recognized small animal imaging platform (OPTIMAL) that is part of the IBISA and France Life Imaging (FLI) programs.
Our research is conducted in an interdisciplinary environment where biologists collaborate with chemists, physicists, biotechnology companies and clinical teams.
Our research axes
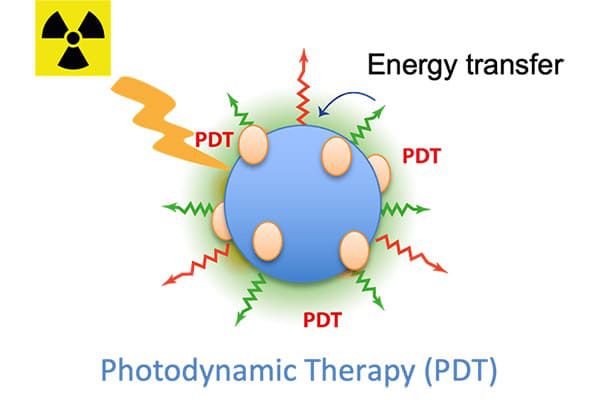
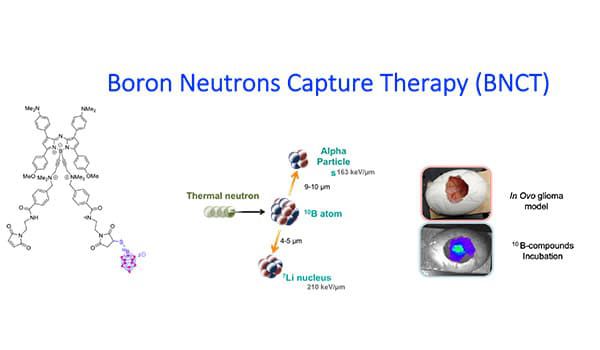
We design various types of fluorescent NP, including some that can be detected in the NIR I or NIR II windows. The anti-cancer effects of these nano-vectors are triggered by X-Rays, Neutrons or Light excitation delivered on the tumor site. These NPs are either metal nanoclusters, nanoscintillators, boron-containing NP or activatable liposomes that can induce x-ray dose-enhancement (RDE), radiosensitization, boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT), photodynamic therapy (PDT) or radiotherapy-triggered drug release.
Learn moreWe characterize the interactions between tumor cells and their microenvironment in order to identify therapeutic targets and to define new therapies and/or therapeutic combinations. We study in particular the EGFR, IGFR and integrins pathways and we develop basic, applied and translational research activities towards the clinic by relying on the dermatology department of the Grenoble Alpes University Hospital.
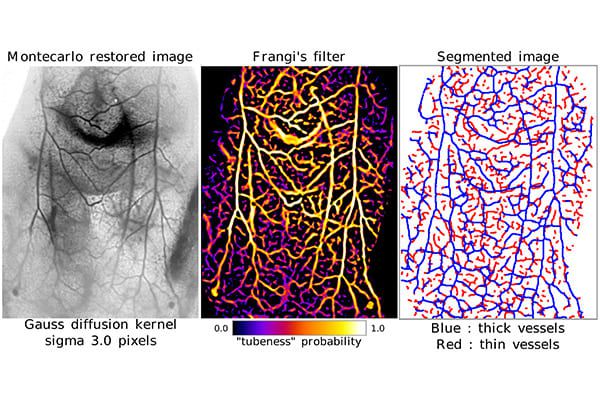
Learn moreWe develop NIR and photoacoustic imaging instruments for in vivo applications. The NIR I and NIR II optical windows enable deep non-invasive imaging, allowing us to probe physiological and molecular processes at high resolution. For diagnostic purposes we are developing LIBS (laser induced breakdown spectroscopy) elemental microscopy to image the chemical composition of tissue sections. Elemental maps can be obtained in particular for detection of metallic nanoparticles.
Learn moreOur major publications
See all publicationsOur activities in pictures
Our technologies
- 2D and 3D (spheroids and organoids) cell culture
- Chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay
- Animal models
- NIR imaging in vivo
- Optical guided surgery
- Innovative (radio)therapies
- Multi-elemental LIBS microscopy Learn more